Hydrocarbon field has a long life cycle: From the discovery of a petroleum deposit to the first oil/gas, exploration and production activities are spread over several decades.
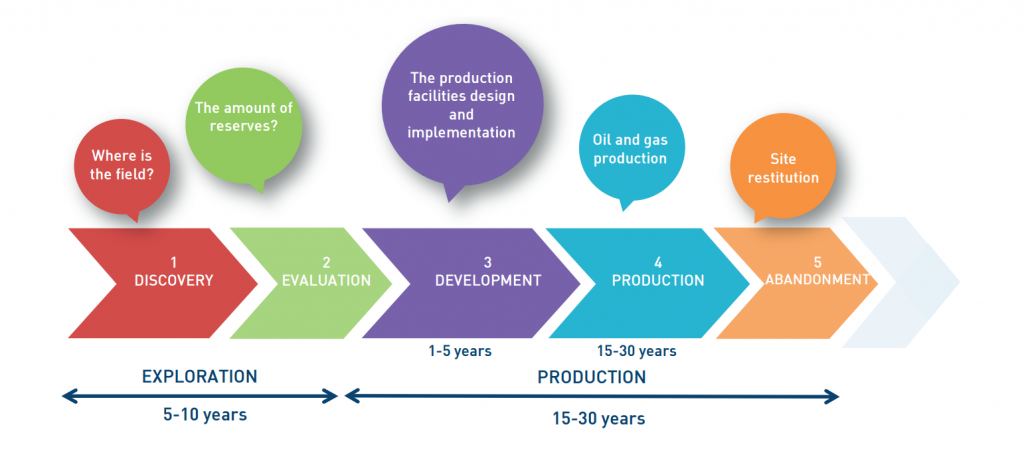
Five main steps can be distinguished in the life of an oil or gas field:
EXPLORATION AND EVALUATION
1 | Field discovery
- Oil and gas are trapped in reservoir rocks buried underground (on shore/ off shore),
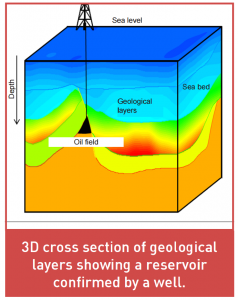
- To locate hydrocarbon accumulation, geoscientists analyze images of the earth’s subsurface produced by seismic echography. They build a model of geological layering of the subsurface, and then identify potential reservoirs called «prospects»,
- Exploration wells need to be drilled to check if the identified prospect does indeed contain hydrocarbons. These wells are typically several kilometers deep
2 | Field evaluation
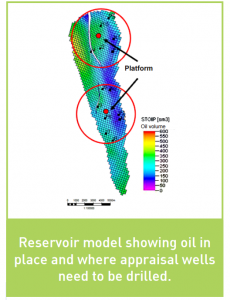
Once discovery has been confirmed, 3D numerical reservoir simulation models are built:
- To estimate the initial volume of oil and gas in the reservoir,
- To simulate the reservoir fluid flow behavior and optimize the field development scenario (number, type and location of wells, level of field production, etc…). Appraisal wells are drilled to improve the field description through further data acquisition.
OIL & GAS PRODUCTION
3 | Field development
A field development plan establishes the following:
- The number of wells to be drilled to reach production objectives,
- The recovery techniques to be used to extract the fluids within the reservoir,
- The type and cost of installations, such as platforms, depending on the marine environment (tides, storms, waves, winds, corrosion, …),
- The separation systems for gas and fluids, > the treatment systems needed to preserve the environment.
4 | Field production
The time period over which hydrocarbons may be extracted varies between 15 to 30 years and may be extended up to 50 years or more for «giant fields». The lifetime of a reservoir is composed of different successive phases:
- A period of production increase,
- A stabilization phase or «plateau»,
- Injection phases (water, gas or chemical products) to «assist» the hydrocarbon recovery and thus maintain a satisfactory volume of produced resources,
- The depletion period when hydrocarbon production declines progressively.
5 | Field abandonment
When the hydrocarbon production rate becomes non economical, the reservoir is abandoned. Before abandoning the field, the oil companies:
- Dismantle facilities such as platforms,
- Put the well in a safe state, Preserve the field’s residual hydrocarbon reserves of the field,
- Clean, depollute and rehabilitate the site.
(Source : IFP SCHOOL)